
In the early 1980s, Philips Semiconductors (now NXP Semiconductors) introduced the I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) protocol, revolutionizing inter-device communication in electronic devices. With just two wires, SDA and SCL, I2C has become a standard for efficient data exchange and control signal transmission.
I2C, or Inter-Integrated Circuit, is a bus interface protocol designed for serial communication. It is widely used for short-distance communication and is also known as Two-Wire Interface (TWI).In this article, we’ll explore the fundamentals of I2C communication, its key features and advantages, structure, components, and delve into advanced techniques and troubleshooting methods.
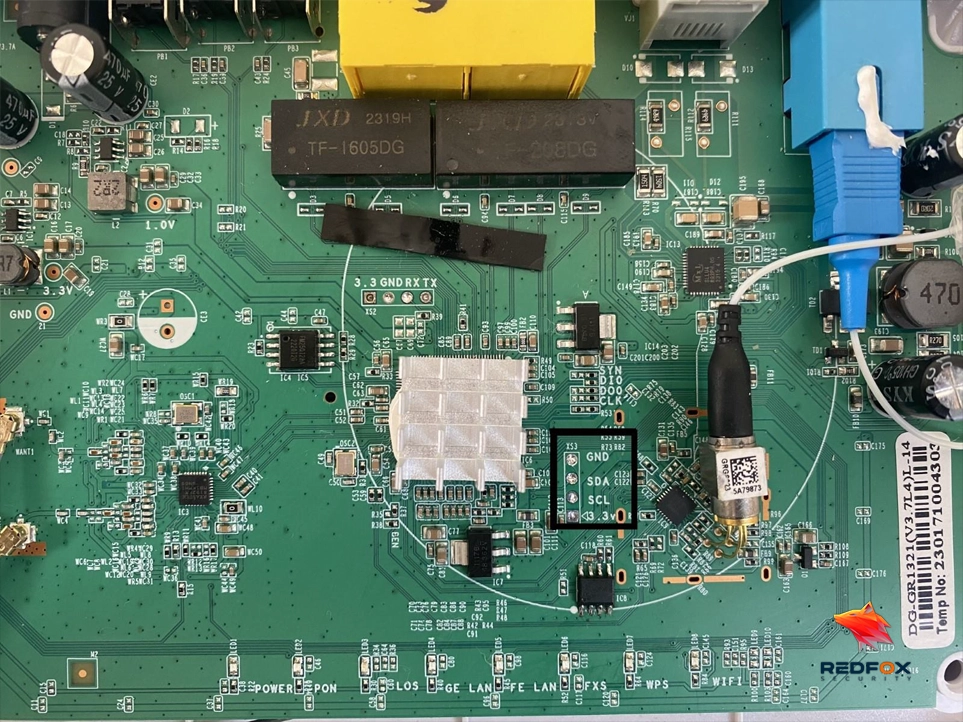
SDA transmits the actual transmission, while SCL acts as clock pulses synchronizing its transfer. Furthermore, clock signals governing communication speed are controlled by this controller device. To facilitate communication on an I2C bus, every device is assigned its address.
This addressing scheme allows master devices to easily recognize and connect with specific agent devices on one bus while accommodating an abundance of devices simultaneously.
Master Mode: Initiates communication.
Slave Mode: Responds to the master.
Data Transmission
Packet Structure
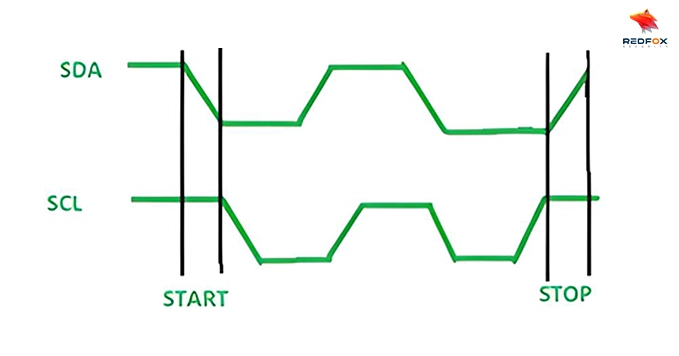
Start and Stop Conditions
Read/Write Bit
ACK/NACK Bit
Addressing
The address frame is the first frame after the start bit. Slave compares its address and sends ACK if matched.
I2C Packet Format
There are 8 bits on the SDA line, and the 9th bit is reserved for ACK/NACK: Initiates communication.
Slave Mode: Responds to the master.
| Feature | I2C Communication Protocol | SPI Communication Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Wires | 2 (SDA and SCL) | 4 (MOSI, MISO, SCK, and SS) |
| Communication Type | Half-duplex | Full-duplex |
| Maximum Devices | Limited by addressing | Limited by chip select (SS) lines |
| Data Transfer Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Error Handling | Improved with ACK/NACK | Not as robust |
| Cost | Cost-efficient | More expensive |
| Complexity | Simpler | More complex |
| Multi-Master Configuration | Yes | Yes |
| Synchronous Communication | Yes | Yes |
| Clock Stretching | Yes | No |
| Arbitration | Yes | No |
Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Protocol is an efficient communication standard that enables effortless data transfer and device control between devices. By becoming acquainted with its basics, features, and structure, you can tap its full potential and realize its full power.
Through this comprehensive guide, we have examined various aspects of the I2C protocol, from its basic communication fundamentals to advanced optimization techniques. We covered start/stop/data transfer processes as well as multi-master arbitration concepts.
Additionally, we’ve reviewed common issues associated with I2C communication and provided solutions to address them effectively. Furthermore, advanced techniques for optimization, as well as invaluable resources and tools, were shared to aid your understanding of the protocol.
Redfox Security is a diverse network of expert security consultants with a global mindset and a collaborative culture. If you are looking to improve your organization’s security posture, contact us today to discuss your security testing needs. Our team of security professionals can help you identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in your systems and provide recommendations to remediate them.
Join us on our journey of growth and development by signing up for our comprehensive courses.