
Subdomain enumeration is a critical process for researchers, security professionals, and enthusiasts delving into web architecture. By uncovering and mapping subdomains, we can gain invaluable insights, uncover digital footprints, and strengthen cyber defences. In this blog, we will outline all tools available for subdomain enumeration that can assist us in mapping this intricate tapestry of online presence.
Subdomains are second-level domains within an overall root domain that serve various functions, including hosting blogs or e-commerce stores within organizations, as well as sub-sites with distinct services or functionalities within them. Subdomains play a vital role in helping organizations effectively structure their online presence by segregating services and functionalities within them.
For example, subdomains, like “maps.google.com” or “news.google.com,” function as distinct entities within a root domain. They play a crucial role in organizing services and functionalities, enhancing an organization’s online structure.
Enumerating subdomains provides multiple advantages for security professionals and organizations alike, making this an essential practice:
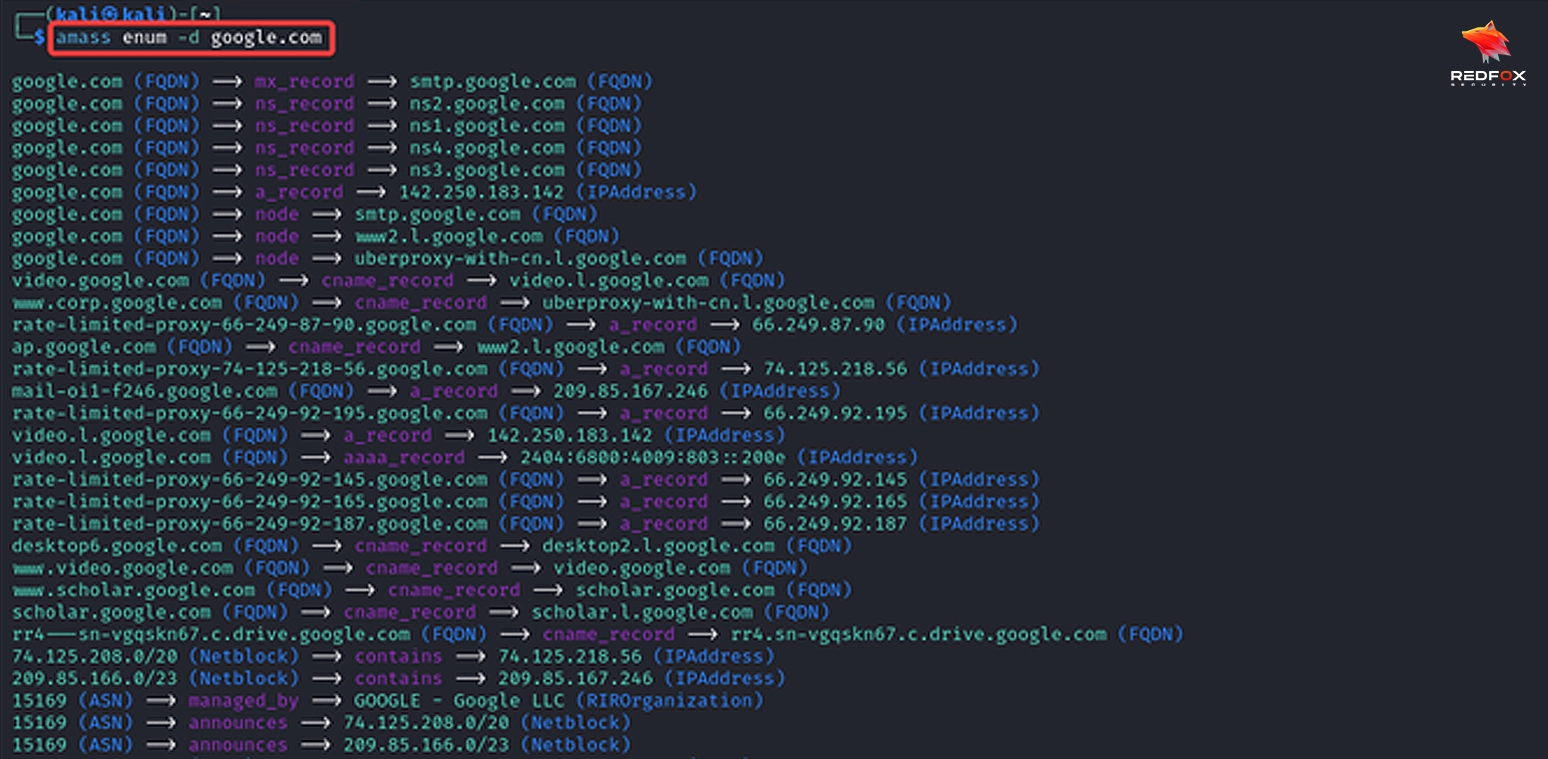
Security professionals can uncover less protected subdomains that may be more exposed than their root domain or target organization to attacks, enabling a proactive approach to security by taking measures before vulnerabilities can be exploited. For example, using DNS brute-forcing to identify vulnerable subdomains before potential attackers can exploit them. Using Subfinder, a security expert identifies “test.google.com” as a less-protected subdomain, prompting pre-emptive security actions.
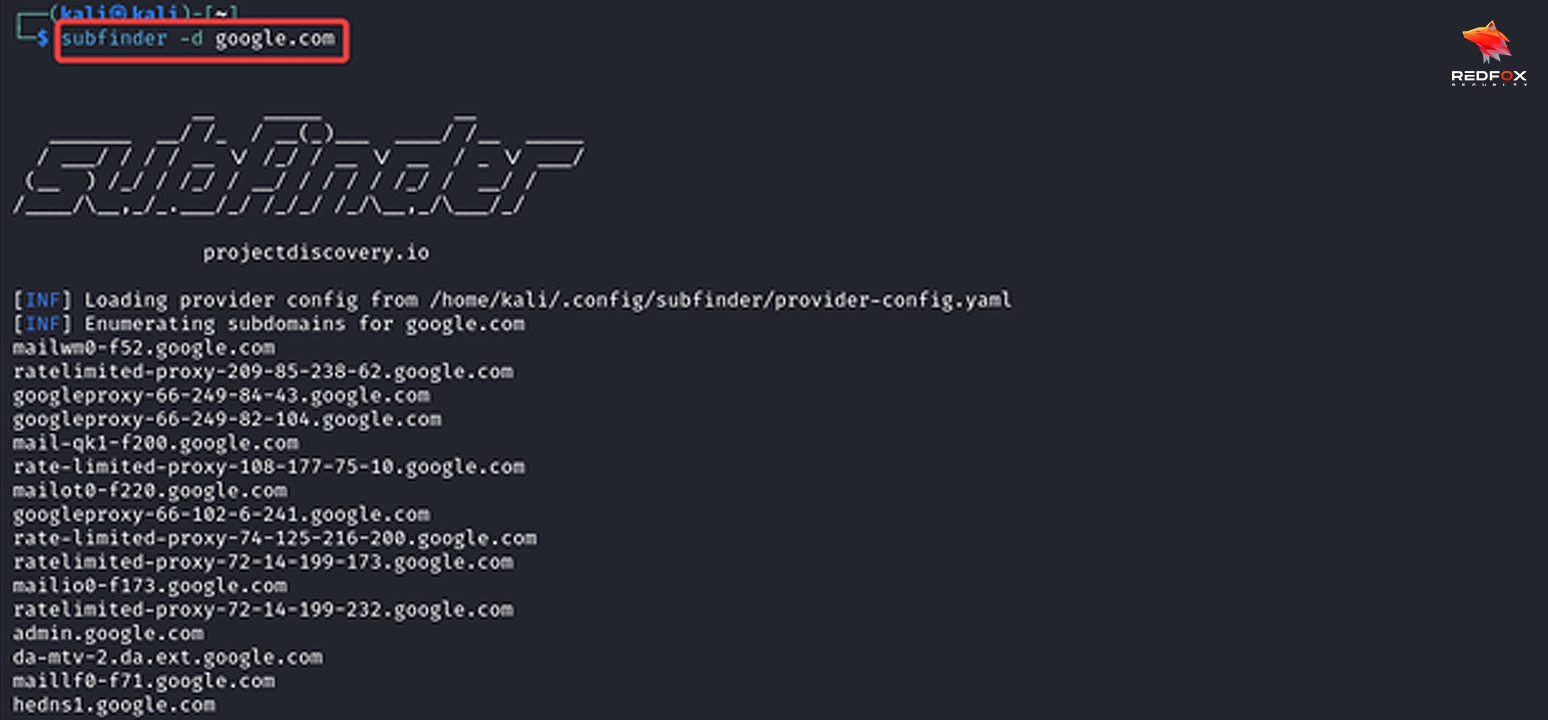
Subdomain enumeration provides vital insights into an organization’s structure, services, and online footprint – providing professionals with valuable data during penetration tests or security assessments, allowing them to fully comprehend their target’s digital landscape.
Organizations may unwittingly expose sensitive information like internal IP addresses through improperly configured DNS entries. Subdomain enumeration allows businesses to quickly recognize such misconfigurations and provide solutions to prevent potential security breaches.
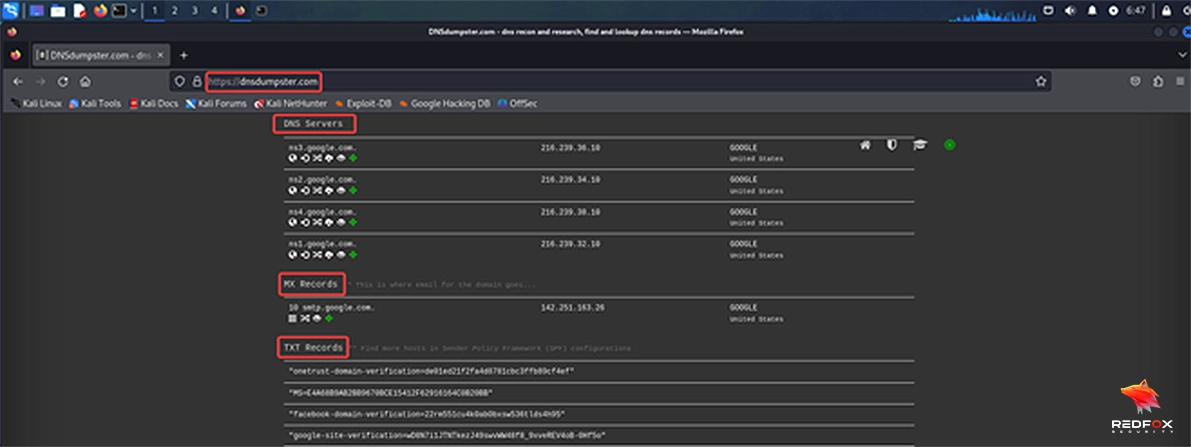
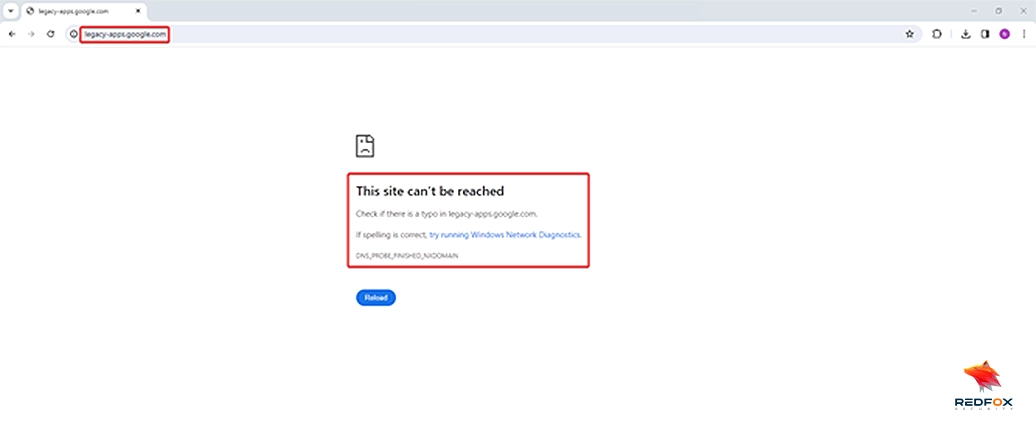
Forgotten or hidden subdomains may host applications that an organization no longer pays attention to or actively maintains; by uncovering these unknown apps, security professionals can assess their vulnerability and mitigate potential risks. Enumeration Techniques can assist with this endeavour. For example, Active enumeration reveals the existence of “legacy-apps.google.com,” hosting outdated applications no longer actively maintained.
Google’s Certificate Transparency initiative seeks to enhance SSL/TLS certificates’ security and was first revealed last December. Security professionals can search CT logs to identify subdomains associated with a target domain, as they offer a public record of all issued SSL/TLS certificates that may help identify new or unexpected subdomains.
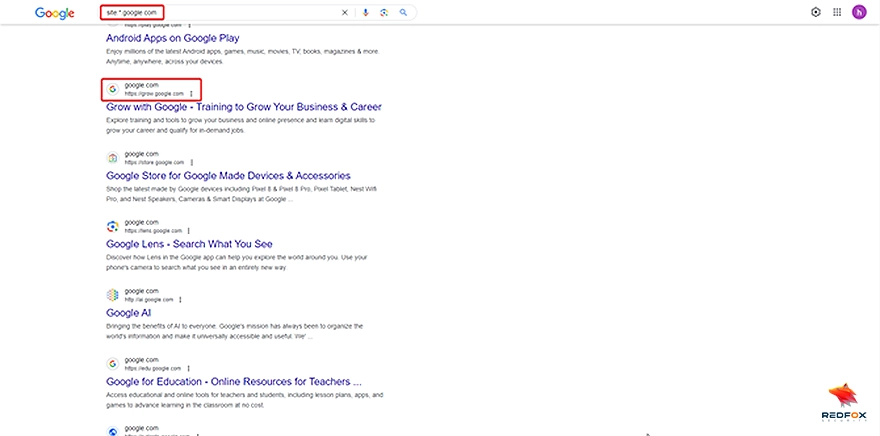
Leveraging the power of Google search, Google Dorking allows professionals to discover information not intended for public access. By employing advanced operators and searching specific file types, professionals can discover subdomains associated with any target domain and identify subdomains associated with each subdomain associated with any target domain. Leveraging Google Dorking, experts can discover unintended information. For example, searching for “site:*.google.com” reveals subdomains like “grow.google.com” & “santatracker.google.com”.
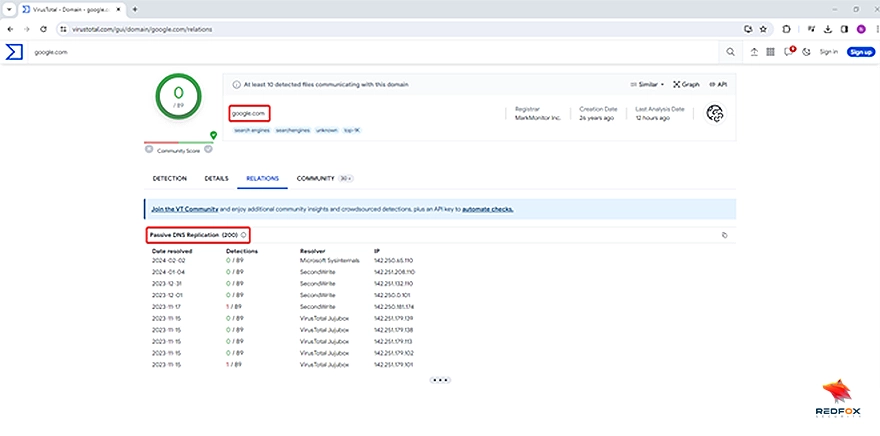
DNS aggregators like VirusTotal Passive DNS Replication and DNSDumpster bring together information from multiple DNS servers into an easily understandable format, providing an all-inclusive view of subdomains associated with an individual target domain.
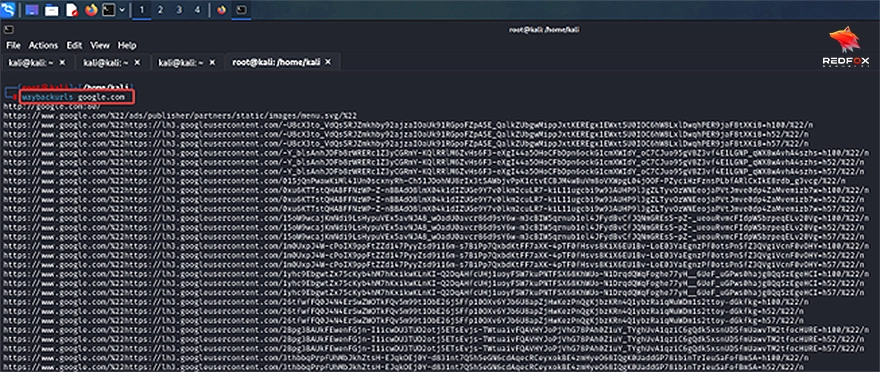
Wayback URLs are a passive subdomain enumeration technique used in cybersecurity to discover subdomains associated with a target domain. It leverages the Wayback Machine, an internet archive service, to retrieve historical snapshots of web pages. The Wayback URLs tool works by querying the Wayback Machine’s database with the target domain as input. It retrieves URLs of archived web pages associated with the domain, including subdomains. These URLs are then parsed to extract unique subdomains. This technique is valuable for reconnaissance and foot printing during security assessments, as it can uncover forgotten or deprecated subdomains that may pose security risks.
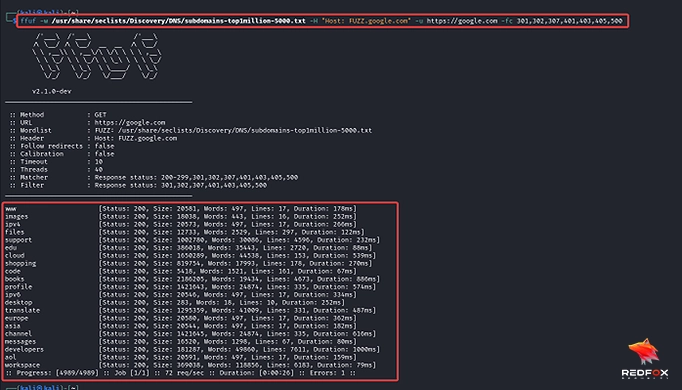
DNS Brute Forcing: DNS brute-forcing involves creating subdomain variations using wordlists and then trying them against DNS servers using tools like FFUF and massdns; these enable professionals to easily identify valid subdomains.
Scraping (JS/Source Code): Scraping is the practice of extracting subdomains from source code and JavaScript files present on web pages using tools like httpx and gospider to facilitate this process. Professionals use such software to crawl websites in order to extract subdomains.
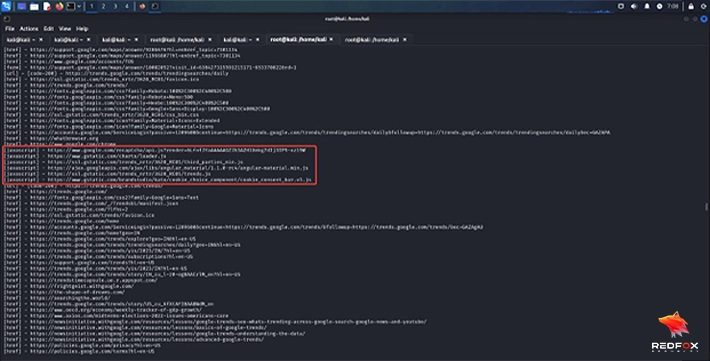
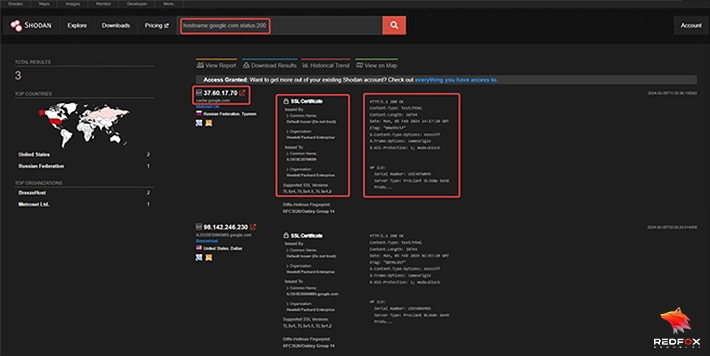
Shodan: Shodan’s main purpose is to collect information on devices and services connected to the internet rather than subdomain enumeration. Shodan employs passive reconnaissance methods for collecting this data, providing some passive subdomain discovery information through passive scanning capabilities. Although Shodan does not specialize in subdomain discovery per se, its capabilities still allow some passive subdomain research capabilities as part of a wider scanning operation.
Subdomain enumeration is invaluable for researchers and security experts, revealing overlooked subdomains, enhancing organizational understanding, and fortifying cyber defenses.
By employing passive, active, and recursive techniques, professionals navigate complex web structures, identify vulnerabilities, and proactively address security risks. With adherence to best practices and up-to-date tools, subdomain enumeration becomes a crucial asset in safeguarding online assets and defending against cybersecurity threats.
Redfox Security is a diverse network of expert security consultants with a global mindset and a collaborative culture. If you are looking to improve your organization’s security posture, contact us today to discuss your security testing needs. Our team of security professionals can help you identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in your systems and provide recommendations to remediate them.
“Join us on our journey of growth and development by signing up for our comprehensive courses.”
Redfox Cyber Security Inc.
8 The Green, Ste. A, Dover,
Delaware 19901,
United States.
info@redfoxsec.com
©️2024 Redfox Cyber Security Inc. All rights reserved.