
Password security is one of the most fundamental pillars of protecting digital systems. Whether it’s a personal device, enterprise network, or critical infrastructure, the way passwords are stored directly impacts the safety of users and organizations alike.
Best practices dictate that passwords should always be encrypted or hashed using industry-standard algorithms, ensuring that even if systems are compromised, sensitive data remains protected. Unfortunately, not all devices follow these principles.
In this blog, we will explore a newly discovered vulnerability in the Digisol DG-GR1321 router that exposes user credentials in plaintext. We’ll break down the technical details of the flaw, discuss its potential impact, provide a proof-of-concept scenario showing how it can be exploited, and outline practical mitigation strategies to help organizations safeguard their networks. By the end, you’ll understand not only why this issue matters but also what steps you can take to reduce your risk.
One such case is the Digisol DG-GR1321 router (Hardware version 3.7L; Firmware version v3.2.02), which has been found to store user passwords in plaintext within its firmware/database.
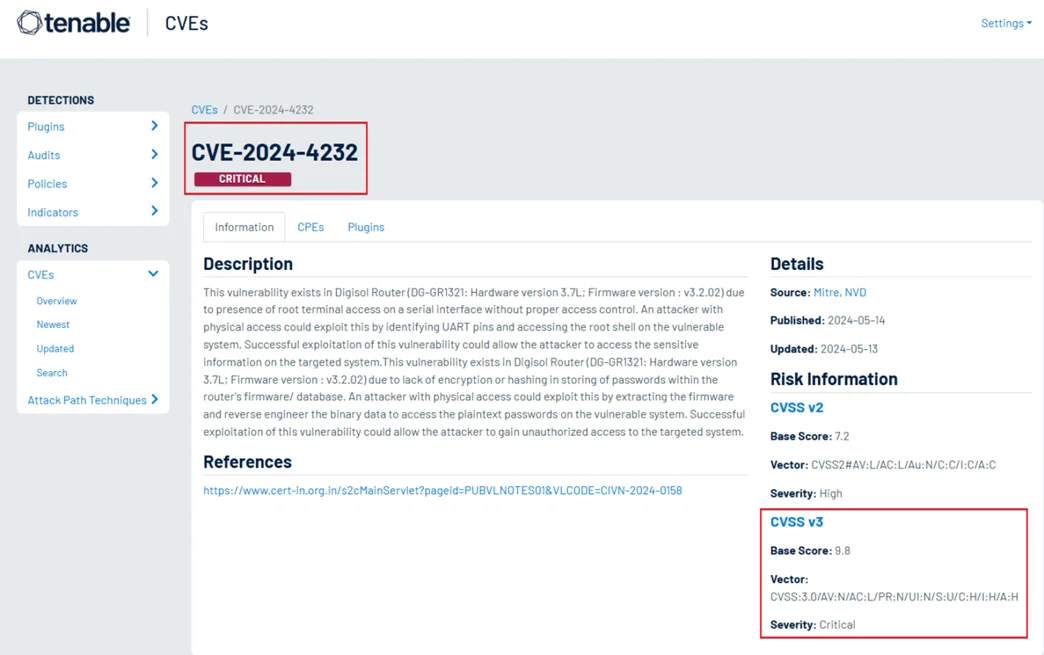
This design flaw represents a severe security risk, bypassing the very protections that secure password storage is meant to enforce. The vulnerability has been officially cataloged as CVE-2024-4232, underscoring its seriousness.
CVE ID: CVE-2024-4232
Vendor/Product: Digisol DG-GR1321 Router
Affected Versions: HW v3.7L; FW v3.2.02
Issue: Passwords stored in plaintext within firmware/database
The implications of this flaw are significant:
Unauthorized Access
Attackers can directly log into the router using extracted plaintext credentials.
Credential Manipulation
Malicious actors could modify or replace login credentials, effectively locking out legitimate users.
Data Exposure
Sensitive information on the router and connected systems is at risk due to insecure storage practices.
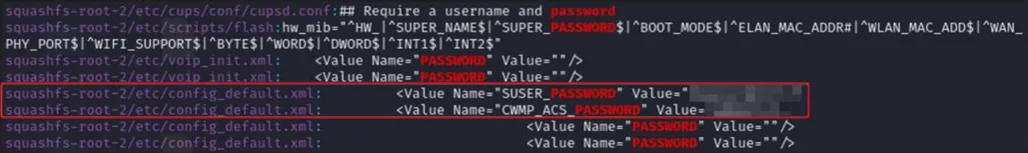
The vulnerability stems from the router’s practice of storing passwords without any form of encryption:
Plaintext Storage – All user credentials are kept in readable form.
Firmware Extraction – Attackers with physical access can dump the firmware image.
Reverse Engineering – Binary analysis of the firmware reveals plaintext credentials.
Exploitation – With these credentials, attackers can alter router settings and compromise the network.
Plaintext Observation: Extracted firmware shows credentials in readable form.
Unauthorized Entry: Attackers can log in using the recovered credentials.
Router Manipulation: Exploitation allows attackers to change configurations and maintain persistent access.
Firmware Update:
Upgrade to the latest available firmware for the DG-GR1321 (HW version 3.7L). Firmware builds starting with V3.1.XX are available through Digisol’s official firmware website or through this Google Drive Link.
Best Practices:
Regularly update router firmware.
Use strong, unique passwords.
Restrict physical access to networking equipment.
The Digisol DG-GR1321 router contains a critical flaw (CVE-2024-4232) where passwords are stored in plaintext, exposing users to unauthorized access, credential tampering, and data leaks. Immediate firmware upgrades are strongly recommended.
At Redfox Security, we are a global team of expert security consultants committed to helping organizations strengthen their defenses. From vulnerability assessments to penetration testing, we work with you to identify weaknesses and provide actionable remediation steps.
Looking to bolster your security posture? Contact us today to discuss how we can help. Additionally, explore our training programs and courses to grow your skills in cybersecurity and join our journey toward building a safer digital ecosystem.