
Routers form the backbone of modern digital connectivity, acting as critical gateways between private networks and the internet. When vulnerabilities are discovered in these devices, the implications extend far beyond individual users—they can compromise entire networks, exposing sensitive data and undermining trust in core infrastructure.
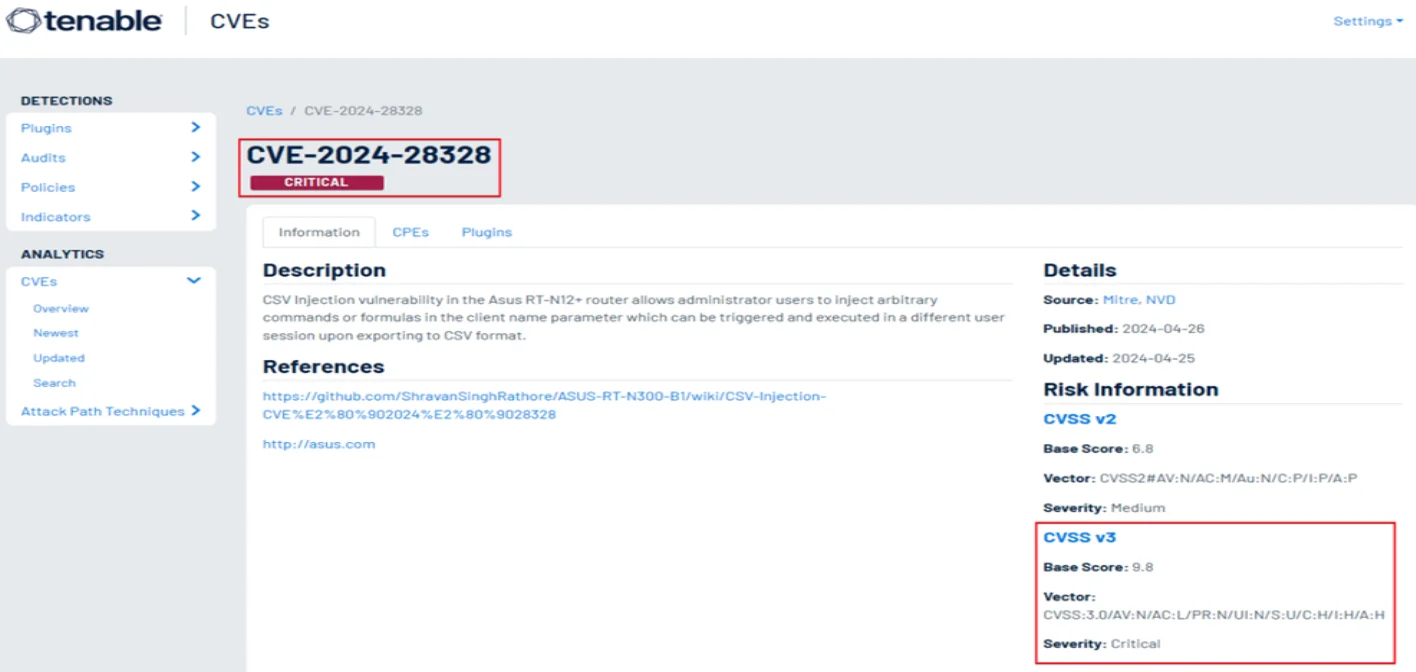
Recently, a security vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-28328, was uncovered in the Asus RT-N12+ B1 (RT-N300 B1) router. The flaw involves CSV Injection, a lesser-known but serious attack vector that can enable malicious code execution, data manipulation, and even unauthorized access across networks. Given the widespread use of this router model in both home and small office environments, this issue highlights the urgent need for proactive security measures, firmware maintenance, and user awareness.
In this blog, we will explore the nature of this vulnerability, its potential impact, the disclosure timeline, proof-of-concept details, and practical steps for mitigation.
21/02/2024 – Initial vulnerability report submitted to Asus.
28/02/2024 – First follow-up communication with Asus.
05/03/2024 – Asus acknowledges the report, noting the RT-N12+ B1 has reached end-of-life and is no longer actively maintained. A beta firmware version is provided for testing. They are seeking user feedback to ascertain if this beta version effectively addresses the identified issue. The beta firmware can be accessed and reviewed via the following link.
01/04/2024 – Second follow-up with Asus.
02/04/2024 – Third follow-up communication.
12/04/2024 – Asus reiterates that firmware updates are difficult due to product end-of-life status but provides a beta firmware version for further testing. You can access the beta firmware file through the following link.
This timeline underscores both the responsiveness of Asus and the challenges of addressing vulnerabilities in discontinued products.
CSV Injection vulnerabilities allow attackers to gain unwarranted access to sensitive information stored within networks. Attackers can compromise the router’s integrity, facilitating unauthorized network access and the execution of arbitrary commands.
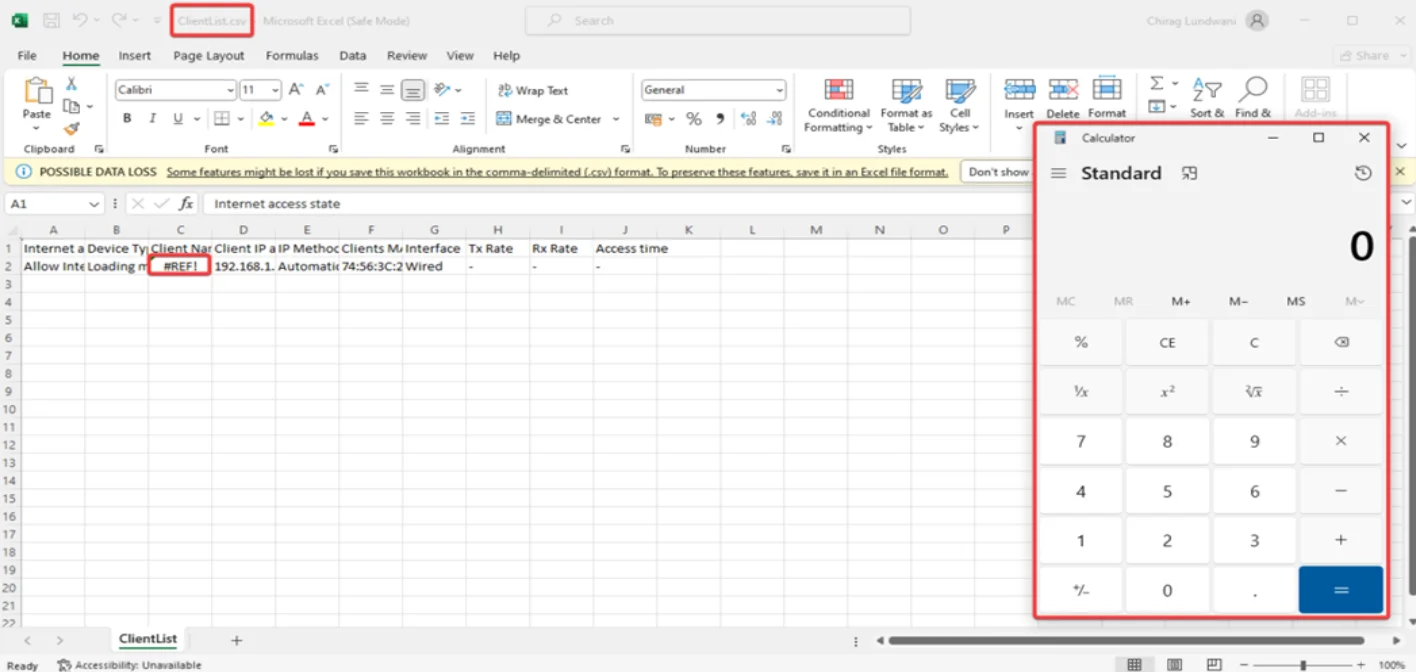
A practical example of this attack involves injecting malicious Excel formulas into the Client Name parameter of the router’s interface. When administrators later export client data to a CSV file and open it in a spreadsheet program, these formulas can execute automatically.
This could lead to:
Data Breaches – Extraction of stored network credentials or sensitive client information.
Service Disruption – Alteration of device configurations or denial-of-service conditions.
Regulatory Risks – Violations of compliance standards due to unauthorized access and data mishandling.
For users of the Asus RT-N12+ B1 router, immediate steps should be taken to minimize risk:
Apply Beta Firmware: Test the firmware update provided by Asus to see if it mitigates the issue. Feedback is critical to ensure effectiveness.
Validate Input Handling: Organizations should ensure proper sanitization of exported CSV data, escaping special characters that may trigger execution.
Consider Device Replacement: Since the router is officially unsupported, migrating to a modern, actively maintained device is the safest long-term option.
Network Monitoring: Implement intrusion detection and log monitoring to detect unusual behavior indicative of exploitation attempts.
The discovery of CVE-2024-28328 in the Asus RT-N12+ B1 router highlights a critical security challenge: legacy hardware that remains widely deployed long after vendor support has ended. While Asus has provided a temporary stopgap in the form of beta firmware, the fundamental issue of end-of-life support underscores the importance of lifecycle management in cybersecurity.
Users and organizations must balance convenience with security, prioritizing upgrades to supported devices and enforcing best practices in input validation and data handling. Vulnerabilities like CSV Injection remind us that even small oversights in data export functions can escalate into serious threats when combined with real-world exploitation techniques.
At Redfox Security, we specialize in uncovering such hidden risks and strengthening defenses before attackers can exploit them. If you want to assess your network’s resilience or enhance your security posture, reach out to our team of experts. Together, we can turn vulnerabilities into opportunities for stronger, safer systems.