
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other objects embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity. It allows them to exchange data and interact over the Internet. Therefore, the basic idea of IoT is to connect all these devices to the Internet, enabling them to share data, communicate, and perform automated tasks without human intervention. This technology is rapidly growing and transforming various industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, transportation, and smart cities.
IoT device protocols vary depending on the application, communication needs, and network infrastructure. Some of the commonly used protocols are:
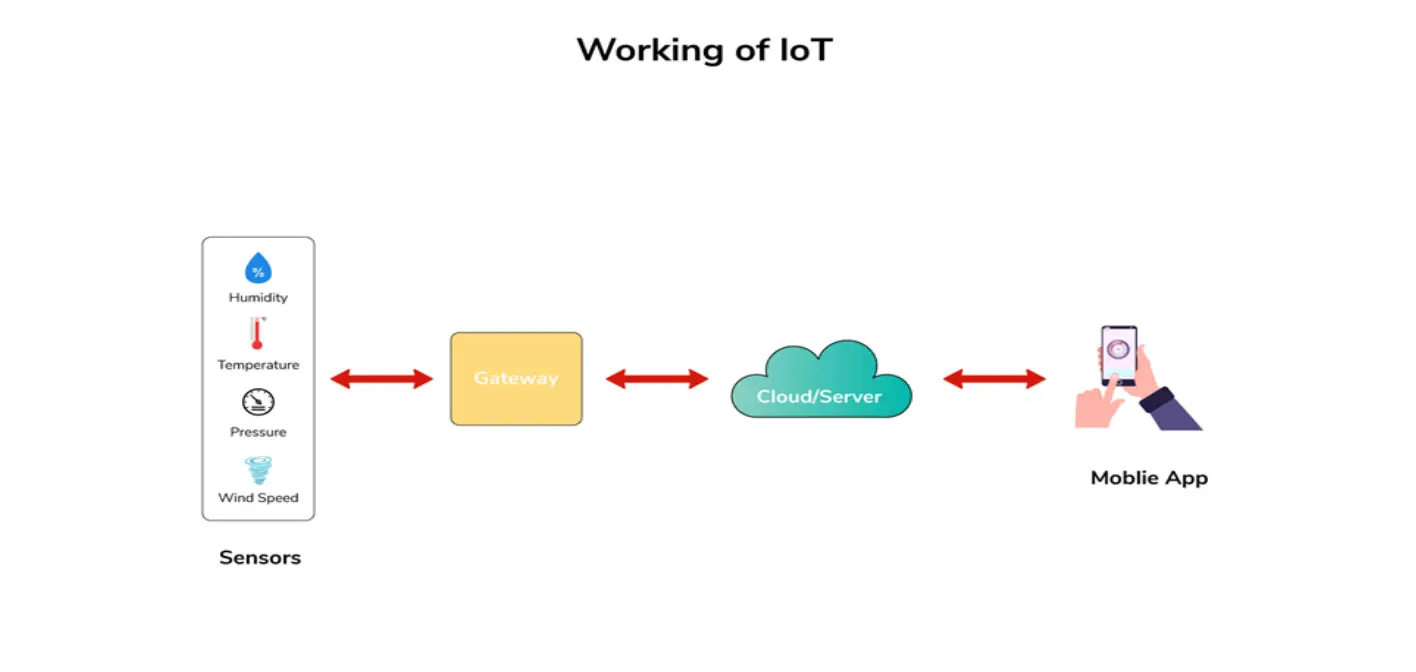
The overview of how IOT works is quite simple and reliable. For example, you have installed an IOT device to predict today’s weather. The first thing that this IOT does is.
The Internet of Things (IoT) has introduced a new set of security challenges due to IoT devices’ interconnected and heterogeneous nature. Some of the security issues that can arise with IoT include:
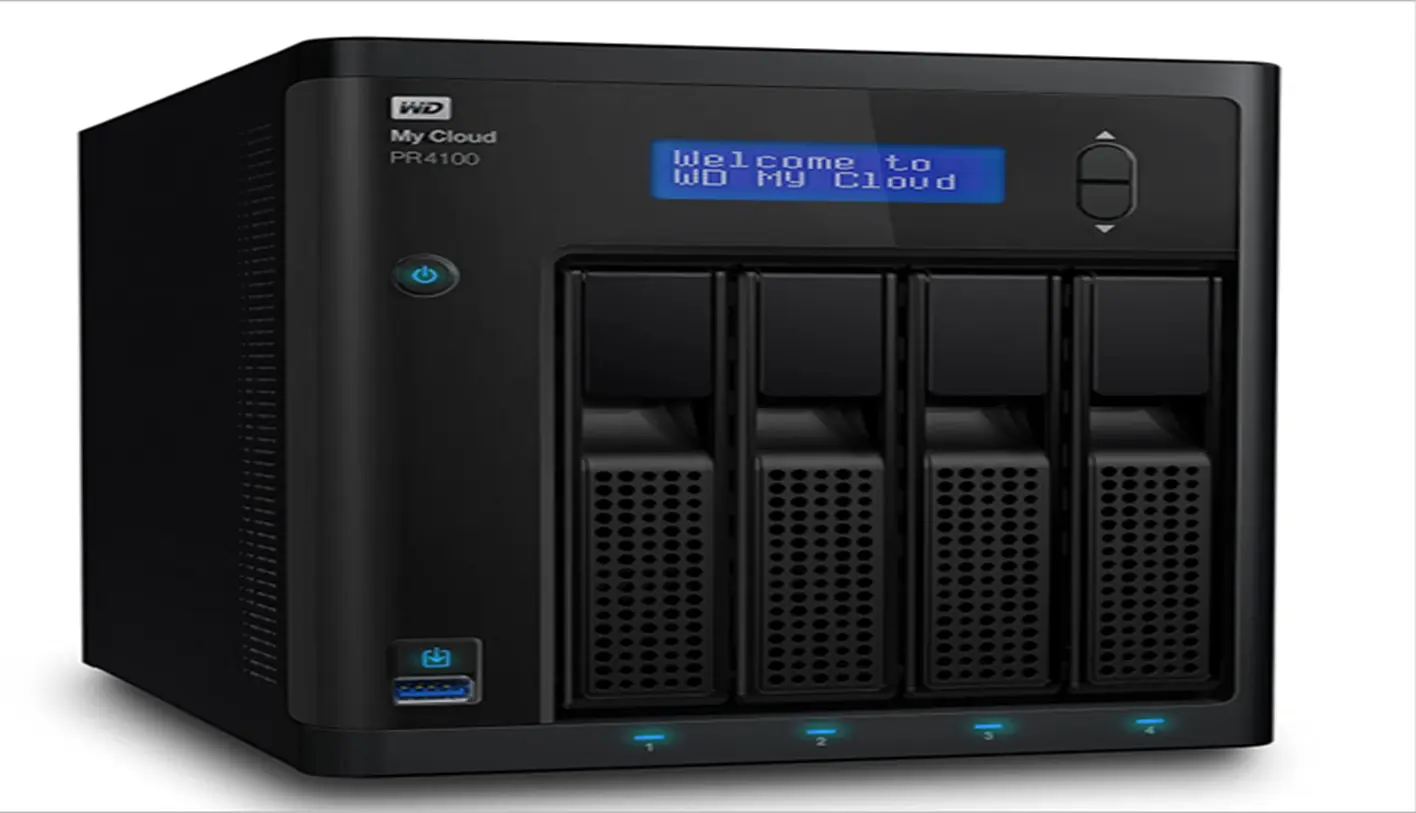
Western Digital My Cloud Pro Series PR4100 (Zero Day)
This zero-day vulnerability was discovered by Pedro Ribeiro and Radek Domanski in Pwn2Own Tokyo 2020 competition in November 2020. The vulnerability affected Western Digital My Cloud Pro Series PR4100 (PR4100) for firmware versions up to 2.40.157.
This vulnerability allowed unauthenticated attackers to access the API hosted on the remote-hosted web server on the device. Using the API allowed attackers to patch the firmware with their maliciously crafted firmware files into the device. The device does not check for the integrity of the firmware file and loads the file to memory during BOOT time. This allowed attackers to create backdoor software to access the device’s internal system whenever possible.

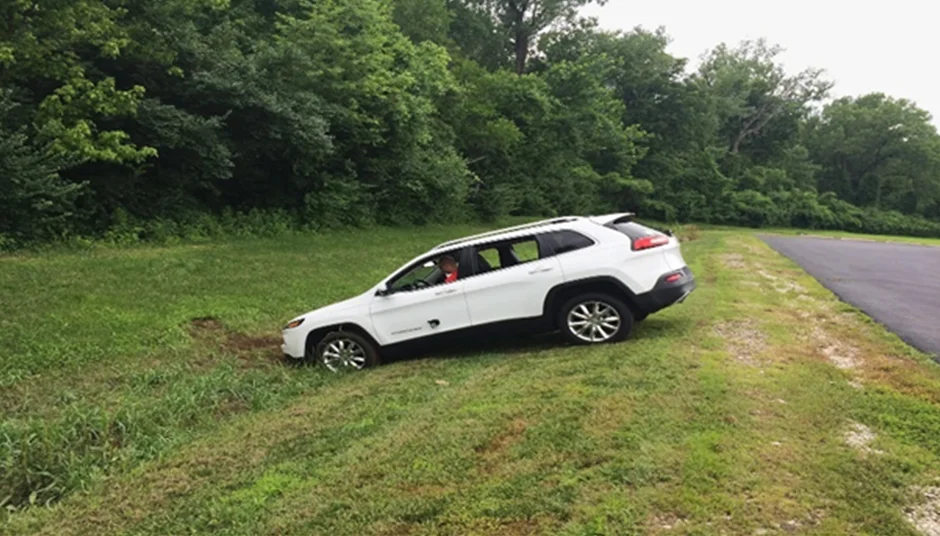
2014 Jeep Cherokee
In 2015, hackers Charlie Miller and Chris Valasek demonstrated at DEF CON 23 how they remotely took control of a 2014 Jeep Cherokee car by accessing its network using Wi-Fi. They cracked the easily-guessable 8-character Wi-Fi password and scanned the network with masscan, discovering that the Uconnect system used the vulnerable D-Bus protocol. As a result, this allowed them to execute commands to the V850 chipset that controlled critical systems like brakes and steering. Such attacks could be catastrophic, especially if autonomous vehicles are targeted.

Thus, from this blog, we have learned that the Internet Of Things(IoT) is a new emerging technology in the market or plans to be fully implemented in large-scale areas or communities such as smart cities. Not to mention, IoT comes with some major security setbacks, such as data privacy, integrity, and software vulnerabilities that can greatly affect the fields which implement it, such as industrial, power plants, and even household.
The most overlooked part about IoT devices is the least frequent firmware updates and easily accessible devices through the Internet, allowing attackers to easily exploit devices with known vulnerabilities even to a large-scale system such as industrial devices.
This blog has given a brief introduction to IoT Security. In the upcoming blogs, we will dive deeper into this space. Stay tuned for more on this.
By partnering with Redfox Security, you’ll get the best security and technical skills to execute a practical and thorough penetration test. Our offensive security experts have years of experience assisting organizations in protecting their digital assets through Penetration Testing Services. To schedule a call with one of our technical specialists, call 1-800-917-0850 now.
Redfox Security is a diverse network of expert security consultants with a global mindset and a collaborative culture. We proudly deliver robust security solutions with data-driven, research-based, and manual testing methodologies.
Join us on our journey of growth and development by signing up for our comprehensive courses.